MSME’s revised structure and registration benefits

First, we will look at the micro, small, and medium enterprises and their structure on and after the F.M. announcement made on the 13th of May, 2020. Honourable Financial minister (F.M.) Nirmala Sitharaman has announced measures to assist businesses, including MSMEs (micro, small, and medium enterprises), to recover from the pandemic’s economic effects. The businesses will need to opt for MSME registration process online that help leveraging the government benefits.
MSME can be classified into two categories.
Manufacturing enterprises – enterprises engaged in the manufacturing or production of goods providing to any industry given in the 1st schedule to industries (development and regulation) act, 1951 and can be defined in terms of investment in plant and machinery.
Service enterprises – enterprises engaged in offering or rendering services and can be defined in terms of investment in equipment.
Structure.
Before 14th of May, 2020, they were defined in terms of investment in plant and machinery or equipment as given below;
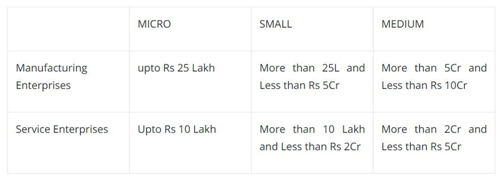
After the 14th of May, 2020, they are defined in terms of investment in the plant and machinery or equipment and according to the turnover as given below;
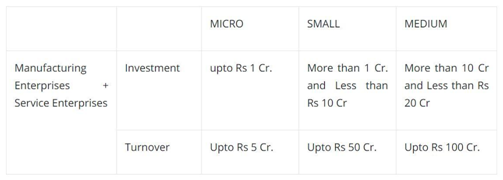
Computation of investment limitation in plants and machinery or equipment for the purpose of MSMED Act, 2006.
– Equipment like dyes, jigs, tools, and spare parts for maintenance and cost of consumable stores.
– Plant and machinery installation.
– R&D (research and development) equipment and pollution-controlled equipment.
– Additional transformer and power generation set installed by the enterprise according to regulations of the state electricity board.
– Service and bank charges will be paid to the NSIC or the state small industries corporation.
– Installation and procurement of cables, bus bars, wires, electric control panels (not mounted on individual machines), miniature circuit breakers or oil circuit breakers that are requisite to be used for offering electrical power to the plant and machinery or for safety measures.
– Gas producer plants.
– Transportation charges (without V.A.T., excise duty, sales tax) for indigenous machinery from its place to site of business.
– Charges paid for technical expertise for establishing plant and machinery.
– Storage tanks that store raw material and finished products that are not aligned with the manufacturing process.
– Firefighting equipment.
Where the trade or traders comes under MSME.
There is no standard universal definition of the term ‘business.’
Nonetheless, usually in its broadest meaning, it consists of all the activity by the community of suppliers of goods or services. The expression ‘business’ is expounded in the income tax act, 1961, as any trade, manufacture, commerce, or any adventure or concern in the nature of trade, commerce, or manufacture.
Section 2(1) (e) of the L.L.P. act, 2008, defines the term business that includes every profession, service, trade, and occupation. Nonetheless, the act does not expound the terms like profession, trade, service and occupation.
As per C.I.T., Trivandrum VS M/S Anand Theatres on 12th of May, 2000, wherein the honourable HC (high court) uttered that the buildings if that plays a crucial role in business operations, then that would come within the inclusive definition of the plant. Hence, herein the term trade will be read as a manufacturer.
Here are the key benefits of MSME registration.
The registration scheme has no legal basis but there is a range of advantages of MSME certification in India. Business units would commonly get registered to get the benefits, support, and incentives given either by the central or state government. Advantages under the MSMED act. Registration of M.S.M. (micro, small and medium) enterprises under the MSMED act is a brilliant way to obtain the center’s incentives. Usually, it contains the following;
– Safeguard against delay in payment from buyers and right of interest on delayed payment.
– Finance will be available easily from banks, without any collateral requirement.
– Octroi benefits and stamp duty.
– Preferences will be given in procuring government orders.
– Concessions in electricity bills.
– Reservations will be provided to production and manufacturing sector enterprises.
– Resolution of disputes promptly with buyers via conciliation and arbitration.
– ISO certification expenses’ reimbursement.
– Credit prescription (Priority sector lending), distinguished rates of interest and so forth.
– Excise exemption scheme.
– Exemption under the direct tax laws.
– Financial help for establishing testing facilities via NSIC.
– Subsidy on ISO certifications.
– Subsidy on NSIC credit ratings and performance.
– Partaking in government purchase registrations.
– Registration in NSIC.
– A counter-guarantee from GoI via CGSTI.
– Weaver in earnest money (security deposit) in government tenders.
– Reduction in rate of interest from banks (subject to ratings).

0 comments